I’m sure all of you can name the 4 taste receptors that scientists have discovered on the tongue: sweet, sour, salty and bitter. However, Ayurvedic medicine has categorized food properties into 6 distinct tastes.
Some of the constitutional doshas require more of certain tastes than others, but it is thought that well-balanced meals encompass all 6 of the Ayurvedic tastes, covering the entire spectrum of food quality. The 6 Ayurvedic tastes are: sweet, sour, salty, bitter, pungent and astringent.
According to Ayurveda, balancing the 6 tastes in the diet aids digestion, ensures physical, emotional and mental well-being and helps decrease aggravation of the dominant dosha of an individual.
About the tastes:
Sweet:We can all easily identify sweet foods, such as honey and fruits. However, sweet taste also includes carbohydrates like rice and other grains, potatoes and milk. Sweet functions include building up tissues and calming nerves.
Sour: Includes acidic fruits such as oranges, lemons and grapefruit, fermented foods (yogurt, kambucha, sauerkraut), alcohol and vinegar. Sour taste acts to cleanse the body and increase the absorption of nutrients.
Salty: Foods that contain salt, from minerals, meat or seaweed. Salt acts to stimulate digestion and improve the taste of food. It also calms nerves and relaxes the mind.
Bitter: Includes dark leafy greens and certain herbs and spices. We often lack enough bitter tasting foods in our Standard American Diet, however, bitter taste is important for detoxification and digestion. According to our Botanical Medicine class, it improves appetite, aids digestion and psychologically “increases one’s appetite for life”.
Pungent: Foods that are spicy, including herbs, peppers and garlic. Pungent tastes increase metabolism and aid digestion.
Astringent: These are foods that produce a “dry” taste in the mouth. Foods that are astringent include legumes, certain fruits, such as apples and pears, certain vegetables, tofu and herbs. Astringent taste helps “dry” fats, thereby aiding weightless, and tightens tissues. In Western Herbalism astringent herbs are used for wound healing and tonifying mucus membranes of the skin, respiratory, urinary and digestive tracts.
Although having a balance of the 6 tastes is beneficial for a healthful diet, increasing certain foods in the diet can help balance the dosha that one is predominant in:
Vata Dosha is balanced by sweet, salty and sour tastes.
Pitta Dosha is balanced by sweet, bitter and astringent tastes.
Kapha Dosha is balanced by bitter, pungent and astringent tastes.
In the Western world we rely heavily on sweet, sour and salty tastes, through a diet high in carbohydrates, processed foods (high salt content) and alcohol (sour). Considering the fact that we live in a Vata-aggravated society, it is comprehensible that our culture gravitates to these tastes more than the other three. However, the leading rise in obesity (Kapha aggravation) could be reflective of the lack of bitter, pungent and astringent tastes in our diets.
In my Ayurvedic course we analyzed various ethnic diets and found that cultures with a set of dietary practices usually include all 6 tastes in their cuisine. We examined Indian, Thai, Persian, Ethiopian and Chinese cuisines, but I also feel that even Italian food represents a balanced diet, according to Ayurveda.
If we take a typical Italian meal – pasta with meat sauce and Insalata Della Nonna– we see that all 6 tastes are represented.
The sweet tastes are represented by the pasta (be it rice pasta, spaghetti squash or another form of pasta), the tomato sauce and some of the vegetables in the salad.
The salty tastes are from the salt and meat added to the sauce.
The sour taste is from the homemade red wine vinegar salad dressing (and the wine!).
The bitter taste comes from the radicchio and fresh garden lettuce in the salad.
The pungent tastes come from the garlic and chili peppers used to make the pasta sauce.
The astringent tastes comes from the fennel and celery in the salad and the apple for dessert.
Dissecting your daily meals for tastes that your diet may be missing is a fun and therapeutic practice. Use it to see how your own diet (whether it is one you have invented for yourself or the one dictated to you by your family or country of origin) may be improved by adding certain flavours. I find it aids me in achieving balance in my own diet, especially when traveling to a new country or designing my own meals. Practicing mindful eating is helpful to detect and distinguish the flavours of your favourite food staples. Chew them slowly and try to decide if the food in your mouth is sweet, salty, sour, bitter, pungent or astringent, or a combination of two or more of these flavours.

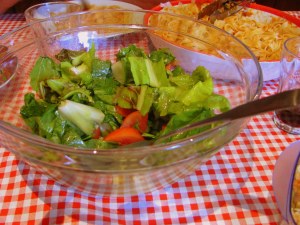
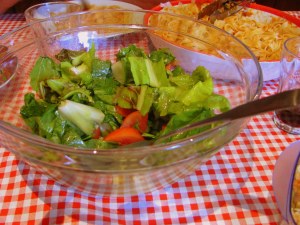






Excellent!
I’m really impressed with your writing skills and also with the layout on your blog. Is this a paid theme or did you customize it yourself? Either way keep up the nice quality writing, it’s rare to see a great blog like this one today.|
Thank you! This is a customized theme (2011 theme) from wordpress.com . I have been tweaking it over the years, but am currently considering self-hosting to be able to use different plug-ins and take my blogging experimentation one step further.
I really like and appreciate your blog post. Much obliged.
Great, thanks for sharing this article.Much thanks again.